Chapter 2 Check Point Questions
Section 2.2
▼2.2.1
Identify and fix the errors in the following code:
1 public class Test { 2 public void main(string[] args) { 3 double i = 50.0; 4 double k = i + 50.0; 5 double j = k + 1; 6 7 System.out.println("j is " + j + " and 8 k is " + k); 9 } 10 }
Section 2.3
▼2.3.1
How do you write a statement to let the user enter a double value from the keyboard? What happens if you entered 5a when executing the following code?
double radius = input.nextDouble();
▼2.3.2
Are there any performance differences between the following two import statements?
import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.*;
Section 2.4
▼2.4.1
Which of the following identifiers are valid? Which are Java keywords?
miles, Test, a++, --a, 4#R, $4, #44, apps class, public, int, x, y, radius
Section 2.5
▼2.5.1
Identify and fix the errors in the following code:
1 public class Test { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 int i = k + 2; 4 System.out.println(i); 5 } 6 }
Section 2.6
▼2.6.1
Identify and fix the errors in the following code:
1 public class Test { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 int i = j = k = 2; 4 System.out.println(i + " " + j + " " + k); 5 } 6 }
Section 2.7
▼2.7.1
What are the benefits of using constants? Declare an int constant SIZE with value 20.
▼2.7.2
Translate the following algorithm into Java code:
Step 1: Declare a double variable named miles with initial value 100.
Step 2: Declare a double constant named KILOMETERS_PER_MILE with value 1.609.
Step 3: Declare a double variable named kilometers, multiply miles and KILOMETERS_PER_MILE, and assign the result to kilometers.
Step 4: Display kilometers to the console.
What is kilometers after Step 4?
Step 1: Declare a double variable named miles with initial value 100.
Step 2: Declare a double constant named KILOMETERS_PER_MILE with value 1.609.
Step 3: Declare a double variable named kilometers, multiply miles and KILOMETERS_PER_MILE, and assign the result to kilometers.
Step 4: Display kilometers to the console.
What is kilometers after Step 4?
Section 2.8
▼2.8.1
What are the naming conventions for class names, method names, constants, and variables? Which of the following items can be a constant, a method, a variable, or a class according to the Java naming conventions?
MAX_VALUE, Test, read, readDouble
Section 2.9
▼2.9.1
Find the largest and smallest byte, short, int, long, float, and double. Which of these data types requires the least amount of memory?
▼2.9.2
Show the result of the following remainders.
56 % 6
78 % -4
-34 % 5
-34 % -5
5 % 1
1 % 5
56 % 6
78 % -4
-34 % 5
-34 % -5
5 % 1
1 % 5
▼2.9.3
If today is Tuesday, what will be the day in 100 days?
▼2.9.4
What is the result of 25 / 4? How would you rewrite the expression if you wished the result to be a floating-point number?
▼2.9.5
Show the result of the following code:
System.out.println(2 * (5 / 2 + 5 / 2)); System.out.println(2 * 5 / 2 + 2 * 5 / 2); System.out.println(2 * (5 / 2)); System.out.println(2 * 5 / 2);
▼2.9.6
Are the following statements correct? If so, show the output.
System.out.println("25 / 4 is " + 25 / 4); System.out.println("25 / 4.0 is " + 25 / 4.0); System.out.println("3 * 2 / 4 is " + 3 * 2 / 4); System.out.println("3.0 * 2 / 4 is " + 3.0 * 2 / 4);
▼2.9.7
Write a statement to display the result of 2 3.5 .
▼2.9.8
Suppose m and r are integers. Write a Java expression for mr 2 to obtain a floating-point result.
Section 2.10
▼2.10.1
How many accurate digits are stored in a float or double type variable?
▼2.10.2
Which of the following are correct literals for floating-point numbers?
12.3, 12.3e+2, 23.4e-2, -334.4, 20.5, 39F, 40D
12.3, 12.3e+2, 23.4e-2, -334.4, 20.5, 39F, 40D
▼2.10.3
Which of the following are the same as 52.534?
5.2534e+1, 0.52534e+2, 525.34e-1, 5.2534e+0
5.2534e+1, 0.52534e+2, 525.34e-1, 5.2534e+0
▼2.10.4
Which of the following are correct literals?
5_2534e+1, _2534, 5_2, 5_
5_2534e+1, _2534, 5_2, 5_
Section 2.11
▼2.11.1
How would you write the following arithmetic expression in Java?
a.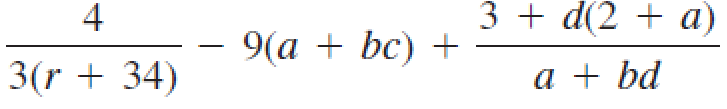
b. 5.5 * (r + 2.5) 2.5 + t
a.
b. 5.5 * (r + 2.5) 2.5 + t
Section 2.12
▼2.12.1
How do you obtain the current second, minute, and hour?
Section 2.13
▼2.13.1
Show the output of the following code:
double a = 6.5; a += a + 1; System.out.println(a); a = 6; a /= 2; System.out.println(a);
Section 2.14
▼2.14.1
Which of these statements are true?
a. Any expression can be used as a statement.
b. The expression x++ can be used as a statement.
c. The statement x = x + 5 is also an expression.
d. The statement x = y = x = 0 is illegal.
a. Any expression can be used as a statement.
b. The expression x++ can be used as a statement.
c. The statement x = x + 5 is also an expression.
d. The statement x = y = x = 0 is illegal.
▼2.14.2
Show the output of the following code:
int a = 6; int b = a++; System.out.println(a); System.out.println(b); a = 6; b = ++a; System.out.println(a); System.out.println(b);
Section 2.15
▼2.15.1
Can different types of numeric values be used together in a computation?
▼2.15.2
What does an explicit casting from a double to an int do with the fractional part of the double value? Does casting change the variable being cast?
▼2.15.3
Show the output of the following code:
float f = 12.5F; int i = (int)f; System.out.println("f is " + f); System.out.println("i is " + i);
▼2.15.4
If you change (int)(tax * 100) / 100.0 to (int)(tax * 100) / 100 in line 11
in Listing 2.8,
what will be the output for the input purchase amount of 197.556?
▼2.15.5
Show the output of the following code:
double amount = 5; System.out.println(amount / 2); System.out.println(5 / 2);
▼2.15.6
Write an expression that rounds up a double value in
variable d to an integer.
Section 2.16
▼2.16.1
How would you write the following arithmetic expression?

Section 2.17
▼2.17.1
Show the output in Listing 2.10 with the input value 1.99.
Section 2.18
▼2.18.1
Can you declare a variable as int and later redeclare it as double?
▼2.18.2
What is an integer overflow? Can floating-point operations cause overflow?
▼2.18.3
Will overflow cause a runtime error?
▼2.18.4
What is a round-off error? Can integer operations cause round-off errors? Can floating-point operations cause round-off errors?