Hints for Java Revel Quizzes and Programming Projects with CodeGrade
Introduction to Java Programming and Data Structures 13E by Y. Daniel Liang

 If you use the AP version of the book, click
here.
If you use the AP version of the book, click
here.
If you need a hint on an exercise that is not listed here, please contact Dr. Liang at y.daniel.liang@gmail.com.
Please check this page often. We update this page frequently in response to student questions. Last update:
.
NOTE: Errata can be viewed at https://liveexample.pearsoncmg.com/erratajava13e.html.
Please send corrections and suggestions to Dr. Liang at y.daniel.liang@gmail.com. We appreciate your help to improve the book.
NOTE: In the expected output pattern of a test run, [\s\S]* represents zero or more number of any characters.
Q1: My program runs fine outside of Revel, but
when running from Revel, it throws java.util.NoSuchElementException. How do I fix it?
A:
It is likely that new Scanner(System.in) is executed multiple times in your code.
You should make it to execute only once.
See Common Pitfall 1: Redundant Input Object at the end of Section 2.19 for a fix. Write your code like this:
public class Exercise {
static Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in)
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Your code
}
// Define optional methods if needed
}
Click here for Revel Videos for instructors and students.
Hints for End-of-Section Programming Quizzes:
Programming Quiz 1.7 Question 1
Hint:
Display exactly the characters as described, case sensitive, words are separately by exactly one space. Display "New coder in Codeville, ready to explore!"
Programming Quiz 1.7 Question 2
Hint:
You need to write a complete class for this exercise. Write the code like this:
public class PyramidVolume {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Write your code here to display the volume. The volume is 200 * 200 * 150 / 3
}
}
Programming Quiz 1.7 Question 3
Hint:
Note that the lines are separated by an empty space line.
Programming Quiz 2.5 Question 3
Hint:
The prompting message is exactly "Enter your daily calorie intake in kcal:" without spaces after :.
The output is exactly "Today your calorie intake was **X** kcal." with a period at the end.
Programming Quiz 2.9.2 Question 3
Hint:
1 km is 1 / Factor parsecs, 2 km is 2 / Factor parsecs, x km is x / Factor parsecs.
Programming Quiz 3.5 Question 2
Change the four bullet items to:
-
If the GPA requirement is not met, it should assign 0 to scholarshipLevel
- If the GPA requirement is met, but the extracurriculars requirement is not met, assign 1 to scholarshipLevel
- If the GPA and the extracurriculars requirement are met, but the community service requirement is not met, assign 2 to scholarshipLevel
- If the GPA, extracurriculars, and community service requirement are all met, assign 3 to scholarshipLevel
Hint:
Your code may look like this:
if (gpa < 3.8)
// WRITE YOUR CODE HERE
else {
if (extracurriculars < 2)
// WRITE YOUR CODE HERE
else {
// WRITE YOUR CODE HERE
}
}
Programming Quiz 3.6 Question 3
Hint:
This code does not work as expected due to numerical inaccuracy.
Rewrite the code using the approximation approach presented in this section
to test if x is very close to 0.5. That is, |x - 0.5| < EPSILON, where EPSILON is a very
small value. Declare a constant EPSILON with value 1E-14, and then rewrite the if statement to correct the potential error. Your code
may look like this:
final double EPSILON = 1E-14;
if (Math.abs(value - 0.5) < EPSILON)
message = "Comparison succesful!";
Programming Quiz 3.14 Question 2
Hint:
Write the code like this:
System.out.println(
// Use ternary operator
);
Programming Quiz 4.4 Question 2
Hint:
If singal.trim().length() is 0, firstChar will be '\0', else firstChar is singal.trim()'s first character.
Programming Quiz 4.4.3 Question 2
Hint:
Use the ternary operator ? : to simplify coding in this exercise.
Programming Quiz 4.4.7 Question 2
Hint:
Use compareToIgnoreCase method.
Programming Quiz 5.2 Question 3
Hint:
Only print the numbers that are multiple of 5. Print each number in a separate line.
Programming Quiz 5.3 Question 2
Hint:
Only print the count (no other output) in this exercise.
Programming Quiz 5.4 Question 1
Hint:
Only print the sum (no other output) in this exercise.
Programming Quiz 5.6 Question 1
Hint:
Your code should look like this:
int count = 0;
do
{
// Write your code here
} while ( // Write your code here);
Programming Quiz 5.6 Question 2
Hint:
If height is 6, the printout from your code should be the following:
o
o
o
o
o
o
Programming Quiz 5.6 Question 3
Hint:
Your code should look like this:
step = 1;
totalElevation = 0;
int i = 0;
do {
// Write your code here
// Update totalElevation by adding step into it
// Update step. step is initially 1, then 2, 4, 8, etc.
} while ([write your code here]);
// After the loop, totalElevation will be 1 + 2 + 4 + 8 + ...
Programming Quiz 5.6 Question 4
Hint:
Your code should look like this:
int un = stdin.nextInt();
int counter = 0;
do {
System.out.println("u" + counter + " = " + un);
// update un
// divide it by 2 if it is even, or multiply it by 3 and add 1 if it is odd.
counter++;
} while (un != 1);
System.out.println("u" + counter + " = " + un);
Programming Quiz 5.7 Question 2
Hint:
If n is 5, your code should print:
u0 = 2
u1 = 1
u2 = 3
u3 = 4
u4 = 7
u5 = 11
Your code may look like this:
int u0 = 2;
int u1 = 1;
int un = 0;
System.out.println("u0 = " + u0);
System.out.println("u1 = " + u1);
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
// write your code here.
}
Programming Quiz 5.7 Question 3
Hint:
n is already declared and initialized in the code. If n is 100, your code should print:
21 51 81
Programming Quiz 5.7 Question 5
Hint:
Your code should look like this:
int number1 = stdin.nextInt();
int number2 = stdin.nextInt();
int gcd = 1;
// write your code here
System.out.println(gcd);
Programming Quiz 7.2.4 Question 5
Hint:
Your code should look like this:
fibonacci[0] = 0;
fibonacci[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i < fibonacci.length; i++) {
// WRITE YOUR CODE HERE
}
Programming Quiz 7.2.6 Question 1
Hint:
Your code should look like this:
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Enter the number of fuel tanks: ");
int numTanks = scanner.nextInt();
double[] tanks = // WRITE YOUR CODE to here to create the array
for (int i = 0; i < numTanks; i++) {
System.out.println("Amount in tank " + (i + 1));
tanks[i] = // WRITE YOUR CODE to here to assign the input to tanks[i]
}
Programming Quiz 7.2.6 Question 2
Hint:
Get the average in all tanks and assign the average to each tank.
Programming Quiz 7.10 Question 1
Hint:
Write your code like this:
public static int findNearestPort(int[] ports, int target) {
int closestIndex = -1;
int minDifference = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// WRITE YOUR CODE to compare the difference |target - ports[i]| and find the minimum among the differences.
return closestIndex;
}
Programming Quiz 7.10 Question 2
Hint:
Write your code similar to binary search like this:
public static int findNearestPort(int[] ports, int target) {
int low = 0;
int high = ports.length - 1;
int closestIndex = -1;
int minDifference = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
// WRITE YOUR CODE to update minDifference and closestIndex
if (ports[mid] < target)
low = mid + 1;
else if (ports[mid] > target)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid;
}
return closestIndex;
}
Programming Quiz 7.10 Question 3
Hint:
In this exercise, you are not looking for the closest element in ports to target, rather any
element whose difference to target is <= tolerance.
Write your code like this:
public static int findWithinTolerance(int[] array, int target, int tolerance) {
int low = 0;
int high = array.length - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (WRITE YOUR CODE HERE) // If target is close to the element within tolerance
return mid;
else if (array[mid] < target)
low = mid + 1;
else
high = mid - 1;
}
return -1;
}
Programming Quiz 8.2.2 Question 1
Hint:
This quiz is to write an expression. Don't use a semicolon in your code.
Programming Quiz 8.2.2 Question 2
Hint:
This quiz is to write an expression. Don't use a semicolon in your code.
Programming Quiz 8.2.2 Question 3
Hint:
This quiz is to write an expression. Don't use a semicolon in your code.
Programming Quiz 8.2.2 Question 4
Hint:
This quiz is to write an expression. Don't use a semicolon in your code.
Programming Quiz 8.3.2 Question 1
Hint:
This quiz is to write an expression. Don't use a semicolon in your code.
Programming Quiz 8.3.2 Question 2
Hint:
This quiz is to write an expression. Don't use a semicolon in your code.
Programming Quiz 8.3 Question 1
Hint:
The square matrix has a major diagonal and sub-diagonal. The major diagonal is arr[0][0],
arr[1][1], arr[2][2], and arr[n-1][n-1]. The sub-diagonal is arr[0][n-1],
arr[1][n-2], arr[2][n-2], and arr[n-1][0]. Here, n is arr.length().
Programming Quiz 8.3 Question 2
Hint:
A two dimensional array is uniformed, if each row has the same size.
Programming Quiz 8.3 Question 3
Hint:
Write your code as follows:
int maxSum = -2147483648; // To store the sum of a column with the max total
// See Table 2.1 in Section 2.9 for -2147483648
int maxColIndex = 0; // To store the index of the max-sum column
// Write a loop, for each column, get the sum and compare with maxSum to update maxSum and maxColIndex
// Swap the the first column with the colum at index maxColIndex
Programming Quiz 8.3 Question 4
Hint:
Write your code as follows:
int maxElement = -2147483648; // To store the max element
// See Table 2.1 in Section 2.9 for -2147483648
int maxRow = 0; int maxCol = 0; // To store the row and column index of the max element
// Write a loop to find maxElement, maxRow, and maxColumn
Programming Quiz 8.3 Question 5
Hint:
Write your code as follows:
int rows = arr.length;
int cols = arr[0].length;
int[][] transposedArr = new int[cols][rows];
// assign arr[j][i] to transposedArr[i][j]
Programming Quiz 8.3 Question 6
Hint:
Write your code as follows:
int rows = arr.length;
int cols = arr[0].length;
int[][] shiftedArr = new int[rows][cols];
// Assign the shifted result to shiftedArr. Only shift the columns, not the rows.
// shiftedArr[i][(j + n) % cols] = arr[i][j];
Programming Quiz 9.4 Question 1
Hint:
The constructor should print the sentence "Created a new garden key.". Note the period after the sentence.
Programming Quiz 9.4 Question 3
Hint:
The constructor you need to write is Recipe(Recipe other). In the body, first, create an array and assign it to ingredients as
ingredients = new String[other.ingredients.length];
Second, use the arraycopy method to copy from other.ingredients to ingredients.
Third, assign other's isVegetarian to isVegetarian as
isVegetarian = other.isVegetarian;
Programming Quiz 9.5 Question 1
Hint:
Declare selectedDocument of the Document type. Create and assign new Document() to it.
Programming Quiz 9.5.1 Question 1
Hint:
The sensor object's collectData method has one int argument that specifies the station. So, invoke sensor.collectData(5) to
collect data for station 5.
This quiz is to write an expression. Don't use a semicolon in your code.
Programming Quiz 9.5.1 Question 3
Hint:
First create a console input object:
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
Second, declare the variables to store input:
boolean didFertilize;
int lastFertilization;
Now, write a loop to read a boolean value to didFertilize and an integer to lkastFertilize, invoke the endDay method.
If it returns true, the loop ends and display "Day Ended". If the method returns false, display "Fertilication Needed" and loop continues.
while (true) {
didFertilize = input.nextBoolean();
lastFertilization = input.nextInt();
if (fertilizerLogger.endDay(didFertilize, lastFertilization)) {
System.out.println("Day Ended.");
break;
}
else {
System.out.println("Fertilization Needed.");
}
}
Programming Quiz 9.7 Question 1
Hint:
Write the code as follows:
// Define public constant, DEFAULT_POPULATION_SIZE, initialized to MEDIUM_POPULATION
// Define public constant, DEFAULT_ANIMAL_SIZE, initialized to SMALL_ANIMAL
// Define public constant, DEFAULT_ANIMAL_DIET, initialized to HERBIVORE
// Write the public no-arg constructor that assigns to maxPopulation
// the DEFAULT_POPULATION_SIZE, to animalSize the DEFAULT_ANIMAL_SIZE,
// and to animalDiet the DEFAULT_ANIMAL_DIET.
public Habitat() {
// Write your code here
}
Programming Quiz 9.7 Question 2
Hint:
You will write the public void reset() method like this:
public void reset() {
// Write the code to reset the values for maxPopulation, animalSize, and animalDiet to their default values.
// Write the code to set surfaceArea to maxPopulation * Habitat.computeMinimumArea(animalSize, animalDiet).
}
Programming Quiz 9.7 Question 3
Hint:
You will write the code like this:
// First, write a private constructor
private Habitat(int newMaxPopulation, char newAnimalSize, char newAnimalDiet, double newsurfaceArea) {
// Write your code to assign these parameters to maxPopulation, animalSize, animalDiet, and surfaceArea.
}
// Then implement the public static method like this:
public static Habitat provisionHabitat(String animal) {
if (animal.equalsIgnoreCase("gray wolf")) {
return new Habitat(9, MEDIUM_ANIMAL, CARNIVORE, 130000000);
} else if
etc... Write your code here
} else if
etc... Write your code here
} else {
return new Habitat();
}
}
Programming Quiz 9.7 Question 4
Hint:
Write four lines of code: 1. declare a Habitat variable named bisonHabitat and write the code that invokes the static method provisionHabitat to create a Habitat for animal "bison" and assign it to the variable.
2. Display the constant value DEFAULT_POPULATION_SIZE.
3. Display the constant value
DEFAULT_ANIMAL_SIZE.
4. Display the constant value DEFAULT_ANIMAL_DIET.
Programming Quiz 9.9 Question 1
Hint:
Work from the template. First, change public to private. Second, write the corresponding getter and setter
methods for these properties.
Programming Quiz 9.9 Question 2
Hint:
Your code should look like this:
public String setFileToUpload(LocalFile file) {
if (file.getSize() > 50000000) {
return "file too big";
}
else if etc...
}
Programming Quiz 9.9 Question 3
Hint:
Your code should look like this:
public class Tool {
private String name;
private boolean active;
private int quantity;
// write the code to implement the getter and setter methods for these properties
// The setters should include checks to prevent setting name to null
// or empty and quantity to negative values. These two setters should return
// a boolean indicating whether the value was successfully changed.
public String getName() {
// Write your code here
}
public boolean setName(String name) {
// Write your code here
}
public boolean isActive() {
// Write your code here
}
public void setActive(boolean active) {
// Write your code here
}
public int getQuantity() {
// Write your code here
}
public boolean setQuantity(int quantity) {
// Write your code here
}
}
Programming Quiz 9.9 Question 4
Hint:
Your code should look like this:
private Artifact artifact;
private Period period;
public Artifact getArtifact() {
// write appropriate code here
}
public void setArtifact(Artifact artifact) {
// write appropriate code here
}
public Period getPeriod() {
// write appropriate code here
}
public void setPeriod(Period period) {
// write appropriate code here
}
Programming Quiz 9.9 Question 5
Hint:
Your code should look like this:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MultimediaLibrary {
private String trackName;
private boolean available;
private int rating;
private Artist artist;
private String[] genres;
// write the code to implement the getter and setter methods for these properties
}
Programming Quiz 11.2 Question 1
Hint:
In the public Dog(String name, int age) constructor, invoke
setName(name) and
setAge(age) to initialize name and age.
Programming Quiz 11.2 Question 2
Hint:
In the public Car(String make, double maxSpeed, String color) constructor, invoke
setMaxSpeed(maxSpeed) and setColor(color) to initialize maxSpeed and color.
Programming Quiz 11.2 Question 3
Hint:
Declare digitalRead with type Ebook and assign an EBook object with title, pages, and format
of "Advanced Java", 350, "PDF".
Declare objectPages with type int. Invoke digitalRead's getPages() method and assign its return value to objectPages.
Programming Quiz 11.2 Question 4
Hint:
Declare wizard with type PlayerCharacter and assign a new object of PlayerCharacter (new PlayerCharacter("Wizard", new double[]{4.0, -5.5}, 10)) to it.
Declare orc with type PlayerCharacter orc and assign a new object of PlayerCharacter (new PlayerCharacter("Orc", new double[]{-4.0, 5.5}, 5)) to it.
You can now invoke wizard's and orc's draw, attack, and erase methods.
Programming Quiz 11.4 Question 1
Hint:
The subclass has a constructor public CreditCardPayment(double amount). Implement it by calling the superclass constructor.
Invoke getAmount() to return the amount to implement the processPayment() method in the subclass. getAmount is defined in the superclass.
Programming Quiz 11.4 Question 2
Hint:
In the implementation of the constructor public PremiumContent(int accessLevel, int bonusAccessLevel), first invoke the superclass constructor
Content(int accessLevel) using the super keyword. Second, set the bonusAccessLevel property value.
Return super.getAccessLevel() + this.bonusAccessLevel to implement the getAccessLevel() method in the subclass.
Programming Quiz 11.11.1 Question 1
Hint:
Write the code in this order:
-
Declare an empty ArrayList object myArrayList and create and assign an empty ArrayList object to myArrayList.
-
Create a Scanner object named (e.g., input) for console input.
-
Keep reading the integers from the input until there is no more input. Test the end of input using input.hasNext(). For each integer read, if
it is divisible by 3, add it to myArrayList.
- Use Collections.sort(myArrayList) to sort the integers in myArrayList in ascending order.
Programming Quiz 12.2 Question 3
Hint:
This exercise is very similar to LiveExample 12.5.
Programming Quiz 12.4.5 Question 3
Hint:
Your code should look like this:
try {
inputHandler.validateInput();
}
catch ([write your code here]) {
[write your code here]
}
catch ([write your code here]) {
[write your code here]
}
Programming Quiz 12.4.5 Question 4
Hint:
Your code should look like this:
try {
post();
}
catch ([write your code here]) {
}
Programming Quiz 12.9 Question 2
Hint:
Your code should look like this:
class InputException extends Exception {
InputException(String message){
[write your code here]
}
}
Programming Quiz 12.9 Question 3
Hint:
The variable thermalShutdown is already declared. Your code should look like this:
thermalShutdown = [write your code here];
Programming Quiz 12.10 Question 1
Hint:
First, create a File object for the file named "errorLog.txt". Second,
invoke File's length() method to get the size of the file.
Programming Quiz 12.11.5 Question 2
Hint:
First, create a File object for the file name in string filename. Second,
invoke File object's exists() and assign the result to fileExists.
Programming Quiz 12.11.5 Question 3
Hint:
Write your code using the following template:
Scanner scanner = null;
try {
File file = new File(fileName);
scanner = new Scanner(file);
count = 0;
// Write a loop here to read lines repeatedly from the file using
// Scanner's nextLine() method and
// accumulate the number of the characters in the line to count
System.out.println("Number of characters in the file: " + count);
}
catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("Error reading file: " + e.getMessage());
}
finally {
if (scanner != null)
scanner.close();
}
Programming Quiz 12.11.5 Question 4
Hint:
Write your code using the following template:
Scanner scanner = null;
try {
File file = new File(fileName);
scanner = new Scanner(file);
wordCount = 0;
// Note words are separated by whitespace characters
// Write a loop here to read words repeatedly from the file using
// Scanner's next() method and
// accumulate the number of the words to wordCount
System.out.println("Total words in the file: " + wordCount);
}
catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("Error reading the file: " + e.getMessage());
}
finally {
if (scanner != null)
scanner.close();
}
Programming Quiz 13.2 Question 1
Hint:
We will add two methods
public void draw() and protected void resize(double scaleFactor) to the class GraphicObject. Since these two methods are only
declared in the class, not implemented, declare them abstract. Now you need also to declare the class abstract.
Programming Quiz 13.2 Question 2
Hint:
Your code should be like this:
public abstract class Media {
private String title;
private String creator;
private int year;
// Implement the constructor
// Implement the displayInfo() method
// Declare abstract method displaySpecialFeature()
}
Programming Quiz 13.2.1 Question 1
Hint:
Your code should be like this:
public abstract class Appliance {
private int powerRating; // Use the default value for powerRating. Don't explicitly initialize it (for example, to 0) due to a CodeGrade grading error.
protected boolean isOn; // Use the default value for isOn. Don't explicitly initialize it anywhere in your code due to a CodeGrade grading error.
// Add constructor, and methods as specified in the description
}
Programming Quiz 13.2.1 Question 2
Hint:
Your code should be like this:
public class Sphere extends Object3D {
// Add data fields, constructor, and methods as specified in the description
}
Programming Quiz 13.5 Question 1
Hint:
Your code should be like this:
public interface Survey {
// Define the methods as specified in the description
}
Programming Quiz 13.5 Question 2
Hint:
Your code should be like this:
interface Sensor {
// Define the abstract methods getTemperature() and getHumidity() as specified in the description
// Define and implement default method isCalibrationNeeded
// Define and implement static method displayActivationMessage()
}
Programming Quiz 13.5 Question 3
Hint:
Your code should be like this:
public class SimpleMediaPlayer implements MediaPlayer {
// Define the data fields, constructor, and methods as specified in the description
}
Programming Quiz 13.5 Question 4
Hint:
Your code should be like this:
public class Task implements TaskAction {
// Define the data fields, constructor, and methods as specified in the description
}
Programming Quiz 18.4 Question 1
Hint:
Step 1: The base case is str.length() <= 1.
Step 2: Now if (str.charAt(0) == str.charAt(1)), you can use a loop to find all consecutive characters same as str.charAt(0).
if (str.charAt(0) == str.charAt(1)) {
while (count < str.length() && str.charAt(0) == str.charAt(count)) {
count++;
}
return str.charAt(0) + Integer.toString(count) + compressString(str.substring(count));
else
return str.charAt(0) + compressString(str.substring(1));
Programming Quiz 18.4 Question 2
Hint:
Declare and initialize variable count to be 0.
Use input.hasNextInt() to test if more input is available. If true, return count + countPositive(input); Otherwise,
return count.
Programming Quiz 18.4 Question 3
Hint:
Declare and initialize variable value to be input.nextInt().
Use input.hasNextInt() to test if more input is available. If true, return Math.max(value, findHighestResponse(input));
Otherwise, return value.
Programming Quiz 18.4 Question 4
Hint:
The base case is str == null || str.length() <= 1. In this case, return str. Otherwise,
return reverseString(str.substring(1)) + str.charAt(0);
Programming Quiz 18.5 Question 1
Hint:
You need to complete this exercise without using the find method in the String class. Write a recursive solution.
The base case is s.length() < 3. In this case, return false.
if (s.startsWith("DBD")) return true. Otherwise, return findPattern(s.substring(1));
Programming Quiz 18.5 Question 2
Hint:
Your code should look like this:
// Helper recursive method to calculate power
private double calculatePower (double base, int exponent) {
// Base case: if exponent is 0, return 1
if (exponent == 0) {
return 1;
}
// Write your code here
}
Programming Quiz 18.5 Question 3
Hint:
Your code should look like this:
// Helper recursive method to calculate power
private double calculatePowerHelper(double base, int exponent) {
// Recursive code here
}
// Public method to calculate power
public double calculatePower(double base, int exponent) {
// Call the helper method with the base and exponent
return calculatePowerHelper(base, exponent);
}
Programming Quiz 18.5 Question 4
Hint:
Your code should look like this:
public static int findMinimum(int[] array, int start, int end) {
if (start == end) {
// Write your code for base case
return array[start];
}
else {
// Write your code for recursion
}
}
Programming Quiz 18.5 Question 5
Hint:
Your code should look like this:
// Helper recursive method to calculate the sum of elements in an array
private int sumArrayHelper(int[] arr, int index) {
// Write recursive implementation for sumArrayHelper
}
// Public method to calculate the average of values in an array
public double calculateAverage(int[] arr) {
// Calculate the sum of elements using the helper method
int sum = sumArrayHelper(arr, 0);
// Return the average by dividing the sum by the number of elements
return (double) sum / arr.length;
}
Hints for End-of-Chapter Assignments (Programming Projects):
Chapter 1: Programming Project 1
You may click Exercise01_01 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Please check your spelling of the words carefully. It is case sensitive. The words are separated by exactly one space.
Chapter 1: Programming Project 2
You may click Exercise01_05 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Write the Math expression as (9.5 * 4.5 - 2.5 * 3) / (45.5 - 3.5).
Chapter 1: Programming Project 3
You may click Exercise01_07 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Use 1.0 instead of 1 in your program.
Chapter 1: Programming Project 4
You may click Exercise01_01Extra to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
In this case, a is 3, b is 4, and c is 5. So, the discriminant for the equation 3x^2 + 4x + 5 is 4 * 4 - 4 * 3 * 5.
Chapter 1: Programming Project 5
You may click Exercise01_02Extra to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
The values for v0, v1, and t are given. Use these values in the formula to compute the average acceleration.
Chapter 2: Programming Project 1
You may click Exercise02_05 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
How would you write this program? Here are some hints:
Step 1: Prompt the user to enter subtotal and gratuity rate into variables subtotal (double) and gratuityRate (double). Note the gratuityRate is in percent. For example, if it is 15%, you enter 15 as the input for gratuityRate.
Step 2: Compute gratuity: gratuity = subtotal * gratuityRate / 100.
Step 3: Compute total: total = subtotal + gratuity.
Step 4: Display gratuity and total. Note you need to first display gratuity and then total. For all the programming projects, please pay attention to output order.
Chapter 2: Programming Project 2
You may click Exercise02_07 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
You must use the int or long type for all variables in this program. See LiveExample 2.5 in Section 2.9 for reference.
Now, the key to solve this problem is to use the correct math.
Step 1: Prompt the user to enter the minutes.
Step 2: Get the totalNumberOfDays from the minutes (i.e., totalNumberOfDays = minutes / (24 * 60)).
Step 3: Get the numberOfYears from the numberOfDays (i.e., numberOfYears = numberOfDays / 365).
Step 4: Get the remainingNumberOfDays from totalNumberOfDays (i.e., remainingNumberOfDays = totalNumberOfDays % 365).
Chapter 2: Programming Project 3
You may click Exercise02_15 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Step 1: Prompt the user to enter two points. Each point has two values for x- and y-coordinates (double).
Step 2: Compute the distance using the distance formula given in the problem description. The correct formula for computing the distance is Math.pow((x2 - x1) * (x2 - x1) + (y2 - y1) * (y2 - y1), 0.5)
Step 3: Display the result.
Chapter 2: Programming Project 4
You may click Exercise02_19 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Step 1: Prompt the user to enter three points. Each point has two values for x- and y-coordinates (double).
Step 2: Compute side1, side2, and side3 using the distance formula given in the preceding project.
Step 3: Compute s using the formula s = (side1 + side2 + side3) / 2.
Step 4: Compute area using the formula given in the problem description.
Step 5: Display the result.
Chapter 2: Programming Project 5
You may click Exercise02_21 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
The annualInterestRate (double) is entered in percentage. In the formula, you need to use monthlyInterestRate (double), which is annualInterestRate / 1200. See LiveExample 2.9 in Section 2.16 for reference.
Chapter 3: Programming Project 1
You may click Exercise03_01 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Step 1: Prompt the user to enter a, b, c. Numbers are double.
Step 2: Compute discriminant.
Step 3: if (discriminant < 0), display "The equation has no real roots".
Step 4: else if (discriminant == 0), compute and display one root.
Step 5: else compute and display two roots.
Common errors from this project: In Step 1, your code should read in float values. In Step 2, discriminant is discriminant = b * b - 4 * a * c. In Step 5, please note that root1 is r1 = (-b + discriminant ** 0.5) / (2 * a). Another common mistake is to compute the roots before the if statement. Please compute roots in Step 5.
Chapter 3: Programming Project 2
You may click Exercise03_03 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Step 1: Prompt the user to enter a, b, c, d, e, f. Numbers are double.
Step 2: Compute detA = a * d - b * c.
Step 3: if (detA == 0), display "The equation has no solution".
Step 4: else compute x and y, and display the result.
Common errors from this project: A common mistake is to compute x and y before the if statement. Please compute x and y in Step 4.
Chapter 3: Programming Project 3
You may click Exercise03_11 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
To test if a year is a leap year, see Section 3.11. Check your spelling on the month names to avoid errors.
Chapter 3: Programming Project 4
You may click Exercise03_21 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Prompt the user to enter year, month, and dayOfMonth. Note that all input are integers. You need to adjust year and month as follows:
if month is 1, set month = 13 and year = year - 1.
if month is 2, set month = 14 and year = year - 1.
You can now use Zeller's formula to compute h.
Chapter 3: Programming Project 5
You may click Exercise03_23 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
A point (x, y) is in the rectangle centered at (0, 0) with width 10 and height 5 if |x| <= 5 and |y| <= 2.5. That is, x <= 5 && x >= -5 && y <= 2.5 && y >= -2.5. x and y are double.
Chapter 4: Programming Project 1
You may click Exercise04_05 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Step 1: Prompt the user to enter numberOfSides as an int.
Step 2: Prompt the user to enter the length of a side as a double.
Step 3: Use the formula to compute the area. Use Math.PI for PI.
Step 4: Display the result.
Chapter 4: Programming Project 2
You may click Exercise04_11 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Step 1: Prompt the user to enter decimal (int).
Step 2: if decimal is < 0 or > 15, display an error as shown in the sample output.
Step 3: else if decimal is < 10, simply display decimal.
Step 4: else display 'A' + decimal - 10.
Chapter 4: Programming Project 3
You may click Exercise04_13 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Step 1: Prompt the user to enter a string into s using input.nextLine().
Step 2: if (s.length() != 1), display an error message as shown in the sample output.
Step 3: Get the first character from the string into ch.
Step 4: Convert ch into uppercase letter.
Step 5: if ch is not a letter, display an error message as shown in the sample output.
Step 6: else if ch is a vowel, display an appropriate message.
Step 7: else display an appropriate message for ch is a consonant.
Chapter 4: Programming Project 4
You may click Exercise04_17 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Prompt the user to enter year (int) and a string for month, and displays the number of days in the month. To test if a string is "Jan", use s.equals("Jan").
To test if a year is a leap year, see Section 3.11.
Chapter 4: Programming Project 5
You may click Exercise04_21 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
You will need to use s.length(), s.charAt(i), and Character.isDigit(ch) method in the program.
Step 1: Prompt the user to enter a string s for SSN.
Step 2: Declare a boolean variable named isValid and assign the conjunction of the following to isValid:
The length of s is exactly 11.
The character at index 0, 1, 2 are digits.
The character at index 3 is '-'.
The character at index 4, 5 are digits.
The character at index 6 is '-'.
The character at index 7, 8, 9 are digits.
Step 3: Display the result based on the value of isValid.
Chapter 5: Programming Project 1
You may click Exercise05_01 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Step 1: Declare and initialize variables. Your program needs to count the number of positives, number of negatives, and total. Think about what initial values are appropriate for these variables. Note that the average can be computed using total / (numberOfPositives + numberOfNegatives).
Step 2: Prompt the user to read a number into variable number.
Step 3: Write a while loop to do the following:
Step 3.1: the loop continuation condition is (number =! 0)
Step 3.2: If number > 0, increase numberOfPositives by 1; if number < 0, increase numberOfNegatives by 1.
Step 3.3: Add number to total.
Step 3.4: Prompt the user to a new input and assign it to number.
Step 4: After the loop is finished, if (numberOfPositives + numberOfNegatives == 0), this means "No numbers are entered except 0". Your program should display exactly this message. Otherwise, display the number of positives, negatives, and average. To compute average, use 1.0 * total / (numberOfPositives + numberOfNegatives).
Chapter 5: Programming Project 2
You may click Exercise05_41 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Maintain two variables (int), max and count. max stores the current max number and count stores its occurrences.
Initially, assign the first number to max and 1 to count. Compare each subsequent number with max. If the number is greater than max, assign it to max and reset count to 1. If the number is equal to max, increment count by 1
Step 1: Declare two integer variables max and count. count is initialized to 0.
Step 2: Read the first number and assign it to max.
Step 3: Write a loop that continues to read an integer. When the integer is 0, the loop ends.
Step 4: For each integer read, if the integer is greater than max, assign it to max and reset count to 1, else if the integer is equal to max, increase count by 1.
Step 5: After the loop is finished, display max and count as shown in the sample run.
Chapter 5: Programming Project 3
You may click Exercise05_09 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Note that we assume that the number of students is at least 2. Use double for score. So use nextDouble() to read a score. So, your program does not need to consider the case for one or no students.
Step 1: Prompt the user to read the number of the students into variable numberOfStudents (int).
Step 2: Prompt the user to read first student name into student1(String) using input.next().
Step 3: Prompt the user to read first student score into score1 (double) using input.nextDouble().
Step 4: Prompt the user to read second student name into student2 (String) using input.next().
Step 5: Prompt the user to read second student score into score2 (double) using input.nextDouble().
Step 6: If (score1 < score2), swap student1 with student2 and score1 with score2. Throughout the program, we will use student1 and score1 to store the student name and score with the highest score and student2 and score1 to store the student name and score with the second highest score.
Step 7: Now write a loop to read the next student name and score. Consider the following cases:
Step 7.1: if (score > score1), assign score1 to score2 and score to score1, student1 to student2 and name to student.
Step 7.2: else if (score1 > score2), assign score to score2 and name to student2.
Step 8: Display the top two students’ name and score.
Chapter 5: Programming Project 4
You may click Exercise05_21 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
For this program, you need to use the formula for computing monthlyPayment and totalPayment in Section 2.16.
Step 1: Prompt the user to read loanAmount (double) and numberOfYears (int).
Step 2: Print the header using System.out.printf("%-20s%-20s%-20s\n", "Interest Rate", "Monthly Payment", "Total Payment");
Step 3: Write a for loop as follows:
Step 3.1: The initial action is to declare and initialize annualInterestRate to 5.0.
Step 3.2: The loop continuation condition is <= 8.0.
Step 3.3: The action after each iteration is annualInterestRate += 1.0/ 8.
Step 3.4: In the loop body, compute monthlyPayment and totalPayment using the formula. Note the monthlyInterestRate is annualInterestRate / 1200. Display annualInterestRate, monthlyPayment, and totalPayment in one line using printf to format the output. Please note: in the first column, you need to put three digits after the decimal point. For example, 5.000% is correct, but 5% is wrong.
Chapter 5: Programming Project 5
You may click Exercise05_49 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Step 1: Declare and initialize variables numberOfVowels and numberOfConsonants with 0.
Step 2: Prompt the user to enter a string using input.nextLine().
Step 3: For each character in the string, do the following:
Step 3.1: Convert the character to uppercase.
Step 3.2: If the character is 'A', 'E', 'I', 'O', or 'U', increase numberOfVowels by 1.
Step 3.3: else if the character is a letter, increase numberOfConsonants by 1.
Step 4: Display the result using the wording as shown in the sample output.
Chapter 5: Programming Project 6
You may click Exercise05_47 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Step 1: Prompt the user to enter the first 12 digits of an ISBN-13 as a string s using input.nextLine
Step 2: If the length of the input is not 12, exit the program using System.exit(1). Note that since REVEL cannot handle System.exit(int), use "return" to replace "System.exit(1).
Step 3: Declare and initialize variable sum. (In Step 4, we will compute sum. sum will be d1 + 3*d2 + d3 + 3*d4 + ... + d11 + 3*d12. Note d1 is s.charAt(0), d2 is s.charAt(1), etc.)
Step 4: for each i from 0 to s.length() - 1, do the following:
Step 4.1: If (i % 2 is 0), add (s.charAt(i) - '0') to sum.
Step 4.2: else, add (s.charAt(i) - '0') * 3 to sum.
Step 5: Obtain checksum that is 10 - sum % 10.
Step 6: Display the entire ISBN-13 string whose last digit is checksum. Note that if checksum is 10, display digit 0.
Chapter 6: Programming Project 1
You may click Exercise06_07 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Step 1: Create a public class named Exercise.
Step 2: Add two methods: the main method and the futureInvestmentValue method.
Step 3: Implement the futureInvestmentValue method to compute the futureInvestment value from investmentAmount, monthlyInterestRate and years using the formula from Exercise 2.21 in Chapter 2. This method return futureInvestmentValue.
Step 4: Implement the main method as follows:
Step 4.1: Prompt the user to enter investmentAmount (double) and annualInterestRate (double).
Step 4.2: Write a for loop as follows: for each year from 1 to 30, display year and the result from invoking futureInvestmentValue(investmentAmount, annualInterestRate / 1200, year). You need to use printf to display formatted output.
Chapter 6: Programming Project 2
You may click Exercise06_13 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Step 1: Create a public class named Exercise.
Step 2: Add two methods: the main method and the m(int i) method.
Step 3: Implement the m(int i) method to return the summation as shown in the formula for m(i) given in the description.
Step 3.1: declare and initialize sum.
Step 3.2: for each k from 1 to i, add k / (k + 1.0) to sum. Note we are using 1.0 rather than 1 to obtain a double result.
Step 3.3: return sum.
Step 4: Implement the main method as follows:
Step 4.1: Display the header of the table using printf. The header is "i m(i)".
Step 4.2: Write a for loop as follows: for each i from 1 to 20, display i and the result from invoking m(i). The result of m(i) is displayed with four digits after the decimal point. So, 0.5 should be displayed 0.5000 using printf.
Chapter 6: Programming Project 3
You may click Exercise06_23 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Step 1: Create a public class named Exercise.
Step 2: Add two methods: the main method and the count(String str, char a) method.
Step 3: Implement the count(String str, char a) as follows:
Step 3.1: declare and initialize count.
Step 3.2: for each i from 1 to str.length() - 1, if str.charAt(i) == a, increase count by 1.
Step 3.3: return count.
Step 4: Implement the main method as follows:
Step 4.1: Prompt the user to enter a string s using input.nextLine().
Step 4.2: Prompt the user to enter a char. To do so, read a line, and assign line.charAt(0) to character ch.
Step 4.3: Simply invoke count(s, ch) to return the count and display the result as shown in the sample run.
Chapter 6: Programming Project 4
You may click Exercise06_25 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
First, please read LiveExample 2.7 ShowCurrentTime.java in Section 2.12. This is very helpful for this exercise.
How would you write this program? Here are some hints:
Step 1: Create a public class named Exercise.
Step 2: Add two methods: the main method and the convertMillis(long millis) method.
Step 3: Implement the convertMillis(long millis) method as follows:
Step 3.1: Obtain seconds from millis.
Step 3.2: Obtain totalMinutes from seconds.
Step 3.3: Obtain minutes from totalMinutes % 60.
Step 3.4: Obtain totalHours from totalMinutes / 60.
Step 3.5: Return a string: hours + ":" + minutes + ":" + seconds.
Step 4: Implement the main method as follows:
Step 4.1: Prompt the user to enter a long value using input.nextLong() into variable totalMillis.
Step 4.2: Invoke convertMillis(totalMillis) to return a string.
Step 4.3: Display this string.
Chapter 6: Programming Project 5
You may click Exercise06_37 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Step 1: Create a public class named Exercise.
Step 2: Add two methods: the main method and the format(int number, int width).
Step 3: Implement the format(int number, int width) method as follows:
Step 3.1: Assign number + "" to a String variable result.
Step 3.2: Obtain the numberOfDigits in number. For example, if number is 231, the numberOfDigits is 3. A simple way of obtaining numberOfDigits is (number + "").length(). number + "" is a string representation for number. Since result is number + "", numberOfDigits is result.length().
Step 3.3: Add width-numberOfDigits number of 0 before result. To accomplish this, write a for loop as follows: for each i from 1 to width - numberOfDigits, do result = "0" + result, which add a digit 0 before result.
Step 3.4: return result.
Step 4: Implement the main method as follows:
Step 4.1: Prompt the user to enter an integer number.
Step 4.2: Prompt the user to enter an integer width.
Step 4.3: Invoke format(number, width) to return a string and display it.
Chapter 7: Programming Project 1
You may click Exercise07_01 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Step 1: Prompt the user to enter numberOfStudents (int).
Step 2: Create an array for scores using new double[numberOfStudents].
Step 3: Declare and initialize variable best to keep the best score. Set the initial value to 0.
Step 4: Prompt the user to enter the scores in a loop that executes numberOfStudents times. For each score entered, store it in scores[i]. Compare it with best. If it is greater than best, assign it to best.
Step 5: Write a for loop for i from 0 to numberOfStudents - 1, compare scores[i] with grade to assign the grade for the student.
Chapter 7: Programming Project 2
You may click Exercise07_03 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Step 1: Create an array for counts using new int[100]. count[0] will store the number of 1s entered and count[99] will store the number of 100 entered. By default, the count[i] is 0.
Step 2: Read a number.
Step 3: Write a while loop:
Step 3.1: The loop continuation condition is (number != 0).
Step 3.2: if number is between 1 and 100, count[number - 1]++.
Step 3.3: read the number again.
Step 4: Write a for loop to display the result as follows:
Step 4.1: for i from 0 to 99
Step 4.2: if counts[i] > 1, display number i + 1, counts[i] and "time" or "times". If (counts[i] > 1), displays "times". If (counts[i] == 1), display "time".
Chapter 7: Programming Project 3
You may click Exercise07_05 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Step 1: Create an array for numbers using new int[10].
Step 2: Declare and initialize an int variable numberOfDistinctValues (int).
Step 3: Write a for loop to execute 10 times. Each iteration of the loop performs the following actions:
Step 3.1: Read an int value.
Step 3.2: Test if value is already in numbers.
Step 3.3: if value is not numbers, add value to numbers: numbers[numberOfDistinctValues] = value.
Step 3.4: Increase numberOfDistinctValues by 1.
Step 4: Display the output: display numberOfDistinctValues and all the elements in numbers.
For Step 3.2, you may write a method
public static boolean isInNumbers(int[] numbers, int size, int value)
This method return true if value is equal to numbers[0], numbers[1], … numbers[size -1].
Chapter 7: Programming Project 4
You may click Exercise07_11 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Step 1: Create a class named Exercise07_11.
Step 2: Add a main method, the mean method, and the deviation method in the class.
Step 3: Implement the mean(double[] x) method as follows:
Step 3.1: Declare and initialize a double variable sum.
Step 3.2: Write a loop to all elements in array x into sum.
Step 3.3: Return sum / x.length;
Step 4: Implement the deviation(double [] x) method as follows:
Step 4.1: Declare and initialize squareSum.
Step 4.2: Write a loop. For each element x[i], add (x[i] - mean(x)) ^ 2 to squareSum.
Step 4.3: return Math.sqrt(squareSum / (x.length - 1))
Step 5: Implement the main method as follows:
Step 5.1: Create an array numbers using new double[10].
Step 5.2: Prompt the user to enter 10 numbers and store them in numbers.
Step 5.3: Invoke mean(numbers) and deviation(numbers) to obtain mean and deviation for numbers.
Chapter 7: Programming Project 5
You may click Exercise07_19 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Step 1: Create a class named Exercise07_19.
Step 2: Add a main method and the isSorted(int[] list) method in the class.
Step 3: Implement the isSorted(int[] list) method as follows:
Step 3.1: Write a for loop: for i from 0 to list.length - 2, if (list[i] > list[i + 1]), return false.
Step 3.2: If nothing is return in the for loop, return true after the for loop.
Step 4: Implement the main method as follows:
Step 4.1: Prompt the user to enter the size of list. Create list using new int[size].
Step 4.2: Prompt the user to enter int values for list.
Step 5: Invoke isSorted(list) to test if the elements in list are sorted.
Chapter 7: Programming Project 6
You may click Exercise07_21 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Arguments from the command line are passed to args in the main method.
How would you write this program? Here are some hints:
Step 1: Declare and initialize sum with 0.
Step 2: Write a for loop. For each args[i], add Integer.parseInt(args[i]) to sum.
Step 3: Display sum.
Chapter 8: Programming Project 1
You may click Exercise08_01 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Step 1: Create a class named Exercise08_01.
Step 2: Add a main method and the sumColumn(double[][] m, int columnIndex)method in the class.
Step 3: Implement the sumColumn(double[][] m, int columnIndex)method as follows:
Step 3.1: Declare and initialize sum.
Step 3.2: Write a for loop: for i from 0 to m.length - 1, add m[i][columnIndex] to sum.
Step 3.3: Return sum.
Step 4: Implement the main method as follows:
Step 4.1: Declare a two-dimensional array m using new double[3][4].
Step 4.2: Write a nested for loop to obtain the input into m.
Step 4.3: Write a for loop. For each j from 0 to m[0].length - 1, invoke sumColumn(m, j) and display it.
Hint: Make sure you use the correct row and column size. The matrix has 3 rows and 4 columns.
Chapter 8: Programming Project 2
You may click Exercise08_05 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Step 1: Create a class named Exercise08_05.
Step 2: Add three methods: a main method, addMatrix(double[][] m1, double[][] m2), and printResult(double[][] m1, double[][] m2, double[][] m3, char op) in the class.
Step 3: Implement the addMatrix(double[][] m1, double[][] m2)method as follows:
Step 3.1: Declare and initialize result using new double[m1.length][m1[0].length].
Step 3.2: Write a nested for loop to assign m1[i][j] + m2[i][j] to result[i][j].
Step 3.3: Return result.
Step 4: Implement the printResult(double[][] m1, double[][] m2, double[][] m3, char op) method as follows:
Step 4.1: For each row i from 0 to m1.length - 1, display a row in m1, m2, and m3. In the middle row, display the op between m1 and m2 and display the = symbol between m2 and m3.
Step 5: Implement the main method as follows:
Step 5.1: Create array m1. Enter input for m1.
Step 5.2: Create array m2. Enter input for m2.
Step 5.3: Obtain m3 from addMatrix(m1, m2).
Step 5.4: Display the result by invoking printResult(m1, m2, m3)
Chapter 8: Programming Project 3
You may click Exercise08_13 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Step 1: Create a class named Exercise08_13.
Step 2: Add two methods:
a main method and
int[] locateLargest(double[][] a)
Step 3: Implement int[] locateLargest(double[][] a) to return the location of the largest element in an array. The first element in the array is the row index and the second is the column index. If there are more than one largest element, return the smallest row index and then the smallest column index.
Step 4: Implement the main method.
Step 4.1: Prompt the user to enter the number of rows and columns of the array.
Step 4.2: Create the array for the array.
Step 4.3: Prompt the user to enter the array.
Step 4.4: Invoke locateLargest(a) method to return the location of the largest element.
Step 4.5: Display the location of the largest element.
Chapter 8: Programming Project 4
You may click Exercise08_25 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Step 1: Create a class named Exercise08_25.
Step 2: Add two methods:
a main method and
boolean isMarkovMatrix(double[][] a)
Step 3: Implement boolean isMarkovMatrix(double[][] a) to test if the array is Markov array.
Step 4: Implement the main method.
Step 4.1: Prompt the user to enter the number of rows and columns of the array.
Step 4.2: Create the array for the array.
Step 4.3: Prompt the user to enter the array.
Step 4.4: Invoke isMarkovMatrix(a) method to return a boolean value.
Step 4.5: Display the result.
Chapter 8: Programming Project 5
You may click Exercise08_21 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
First, a correction in the Sample Run. The Sample Run should be as follows:
Sample Run
Enter the number of cities: 5
Enter the coordinates of the cities: 2.5 5 5.1 3 1 9 5.4 54 5.5 2.1
The central city is at (2.5, 5.0)
The total distance to all other cities is 60.810516285521615
How would you write this program? Here are some hints:
Step 1: Create a class named Exercise08_21.
Step 2: Add three methods: a main method, distance(double[] c1, double[] c2), and totalDistance(double[][] cities, int i).
Step 3: Implement the main method.
Step 3.1: Prompt the user to enter numberOfCities.
Step 3.2: Create cities using new double[numberOfCities][2].
Step 3.3: Prompt the user to enter the coordinates for the cities.
Step 3.4: Declare minTotal (double) and minIndex (int) to store the minimum total distance and the index of the minimum total distance city.
Step 3.4: For every city with index i, invoke totalDistance(cities, i) to return the totalDistance. If it is < minTotal, assign totalDistance to minTotal and i to minIndex.
Step 3.5: Display the minTotal and minIndex for the central city.
Step 4: Implement distance(double[] c1, double[] c2). This method returns the distance between (c1[0], c1[1]) and (c2[0], c2[1]).
Step 5: Implement and totalDistance(double[][] cities, int i). This method returns the total distance from city i to all other cities.
Chapter 9: Programming Project 1
You may click Exercise09_01 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Please follow the template to complete the project.
Chapter 9: Programming Project 2
You may click Exercise09_09 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Please follow the template to complete the project.
Chapter 9: Programming Project 3
You may click Exercise09_13 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Please follow the template to complete the project.
Chapter 10: Programming Project 1
You may click Exercise10_01 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Please follow the template to complete the project.
Chapter 10: Programming Project 2
You may click Exercise10_03 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Please follow the template to complete the project.
Chapter 10: Programming Project 3
You may click Exercise10_11 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Please follow the template to complete the project.
Chapter 10: Programming Project 4
You may click Exercise10_17 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Here are some hints:
1. Use the BigInteger class to create big integer objects. To create a BigInteger for Long.MAX_VALUE, use new BigInteger(Long.MAX_VALUE + "").
2. Find the first n such that n^2 is greater than Long.MAX_VALUE.
3. The ten square numbers are n^2, (n+1)^2, (n+2)^, ... (n+9)^2
Chapter 11: Programming Project 1
You may click Exercise11_13 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Please follow the template to complete the project.
Chapter 11: Programming Project 2
You may click Exercise11_15 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Two possible solutions:
1. You may break the polygon into triangles and compute the areas of the triangles
and add these areas to obtain the area of the polygon.
2. You may use the formula for computing the area of a polygon,
see http://www.mathwords.com/a/area_convex_polygon.htm. When using this formula, please note that
(1) the points entered in the description are in the clockwise order, but the points in the formula are in the counter clockwise order. You need to reverse the input order to apply the formula.
(2) the first point appears at the top and also at the bottom of the formula. If you use an array to store the points, you need to store the points in both the first and last of the array.
Chapter 11: Programming Project 3
You may click Exercise11_17 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Store all smallest factors of m into an array list. n is the product of the factors that appear an odd number of
times in the array list. For example, consider m = 90, store the factors 2, 3, 3, 5 in an array list. 2 and 5
appear an odd number of times in the array list. Thus, n is 10.
Chapter 12: Programming Project 1
You may click Exercise12_13 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
1. Check usage. For all programs that receive command-line arguments, always check usage.
See Section 7.13.
2. Check if the file exists.
3. Use the length() method in the File class to return
the number of characters. This will count all characters including white space characters.
4. Read each word line from the file using input.next(). 5. Close the file and reopen it. Read each line using input.nextLine().
You can test your code using Test1.txt and Test2.txt.
Download these two files from https://liveexample.pearsoncmg.com/test/TestExercise12_13.zip and
Test2.txt. If your output matches the following
two screen shots (character by character), your code is correct.
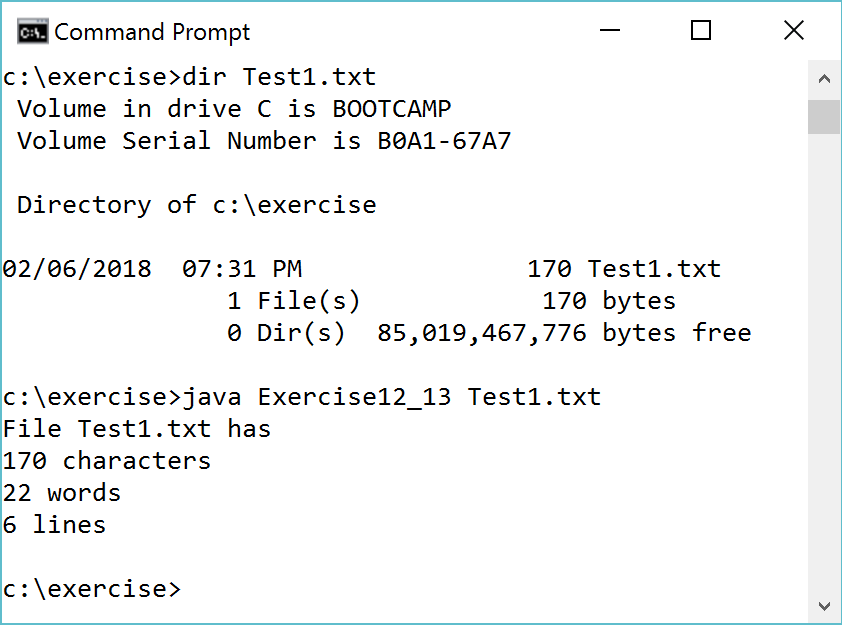
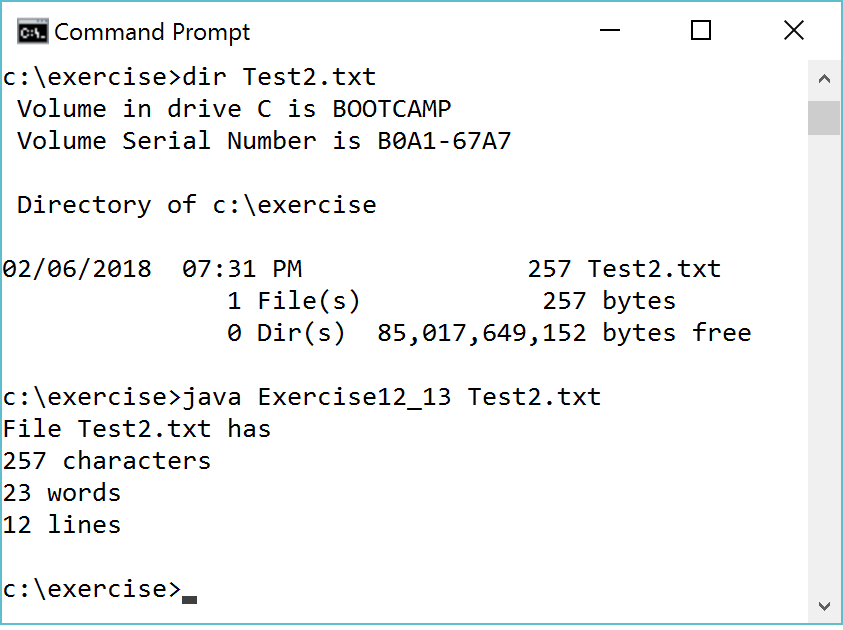
Chapter 12: Programming Project 2
You may click Exercise12_07 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Please read Section 6.7. Section 6.7 gives a program that converts a hex number to a decimal. This program is to convert a
binary to decimal. These two programs are very similar. You just have to make small changes. The radix for hex number 16, but
radix for binary number is 2 for this program.
Throw NumberFormatException if a binary digit is incorrect.
Chapter 12: Programming Project 3
You may click Exercise12_08Extra to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Please follow the template to complete the project.
Chapter 13: Programming Project 1
You may click Exercise13_15 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Please follow the template to complete the project.
Chapter 13: Programming Project 2
You may click Exercise13_17 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Use the code template from the project description to complete the exercise.
Chapter 13: Programming Project 3
You may click Exercise13_19 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Use the code template from the project description to complete the exercise.
Chapter 13: Programming Project 4
You may click Exercise13_21 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Use the code template from the project description to complete the exercise.
Chapter 18: Programming Project 1
You may click Exercise18_01 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
The BigInteger class is introduced in Section 10.9. Please review LiveExample 10.9 for using BigInteger.
Chapter 18: Programming Project 2
You may click Exercise18_03 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
The program contains the main function and the gcd(int m, int n). The main function prompts the user for the input m and n.
It then invokes gcd(m, n) to return the GCD of m and n.
gcd(m, n) returns n
if m % n is 0. Otherwise, gcd(m, n) is return gcd(n, m % n).
Chapter 18: Programming Project 3
You may click Exercise18_08Extra
to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel.
Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
The program contains the main method and the sumOddPositionDigits(long n).
The main method prompts the user for the input number n. It then invokes sumOddPositionDigits(n) to return
the sum of the digits in odd positions in n.
sumOddPositionDigits(n) returns n if n is a single digit.
Otherwise, it returns sumOddPositionDigits(n / 100) + sumOddPositionDigits(n % 10). n % 10 is
the last digit in n. n / 100 is the remaining number after removing the last two digits.
Chapter 18: Programming Project 4
You may click Exercise18_17 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
The program contains the main method and two overloaded count methods. The main method prompts the user for the input string and then a character. It then converts the string into an array of characters by invoking the toCharArray method.
The count(char[] chars, char ch) method invokes count(chars, ch, chars.length - 1).
The count(char[] chars, char ch, int high) is a recursive helper method. The method returns 0 if high < 0. Otherwise, it returns count(chars, ch, high - 1) + (chars[high] == ch ? 1 : 0).
Chapter 18: Programming Project 5
You may click Exercise18_21 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
For simplicity, you can assume that the decimal integer is greater than 0. Your submission will work with this assumption.
The program contains the main method and the dec2Bin method. The main method prompts the user to enter an integer then invokes the dec2Bin(int) to return a binary string for the integer. It displays the binary string.
The dec2Bin(int value) method returns "" if value is 0, otherwise, it returns dec2Bin(value / 2) + value % 2.
Note that dec2Bin(value / 2) returns a string. value / 2 is 0 or 1. dec2Bin(value / 2) + value % 2 is a string.
Chapter 19: Programming Project 1
You may click Exercise19_05 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
There is an error in the description. The method header should be
public static <E extends Comparable<E>> E max(E[] list)
Chapter 19: Programming Project 2
You may click Exercise19_09 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
This program is similar to LiveExample 19.4 in Section 19.5. iveExample 19.4 uses selection sort for arrays. In this program, you need to sort an array list.
Chapter 20: Programming Project 1
You may click Exercise20_10 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Use the code template from the project description to complete the exercise.
Chapter 20: Programming Project 2
You may click Exercise20_23 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Study the code in LiveExample 20.12 in Section 20.11 using some samples, for example, 1+2, 2 * 3 - 3, etc.
Modify the example EvaluateExpression.java incrementally. One step at a time and you will know which step you are struggling.
Step 1. Read the input expression from the console rather than passing from the command line. (The code in the example passes the expression from the command line.)
Step 2. The operator % can be implemented similar to the * and / operators. Add the code for processing % in lines 51-61 in LiveExample 20.12.
Step 3. The operator ^ has the highest precedence. However, note that the ^ operator is right-associative, meaning that 2 ^ 3 ^ 2 is same as 2 ^ (3 ^ 2). In lines 51-61 in LiveExample 20.12, the program processes the * and / operators, add the code for processing the ^ operator after this block.
Watch the last 11 minutes in this VIDEO for additional help.
Chapter 21: Programming Project 1
You may click Exercise21_05Extra to
use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Use TreeSet for this program.
Use addAll, removeAll, and retainAll to perform union, difference, and intersection. You need to clone a set before performing these operations so not to corrupt
the original set.
Chapter 21: Programming Project 2
You may click Exercise21_06Extra to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
See Section 21.6, toward the end of the section, there is a discussion on how to sort the entries on their values using the Collections.sort and Comparator.
Chapter 22: Programming Project 1
You may click Exercise22_01 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
The program contains the main method and the maxConsecutiveSortedSubstring method.
public static String maxConsecutiveSortedSubstring(String s)
Implement the maxConsecutiveSortedSubstring method as follows:
Create an array:
int[] maxConsecutiveLength = new int[s.length()];
Compute the length of the max consecutive subsequence starting at index i for every i and save it in
maxConsecutiveLength[i].
Chapter 22: Programming Project 2
You may click Exercise22_03 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
The program contains the main method and the match method.
public static int match(String s, String pattern)
Implement the match method as follows:
Compare pattern with the substring in s starting from index 0. If a mismatch occurs at index i in s, slide the pattern past the mismatched character in s and continue to compare the
pattern with the substring in s.
Chapter 22: Programming Project 3
You may click Exercise22_05 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Introduce the variables:
int longestSequenceCount = 0;
int longestSequenceValue = 0;
int longestSequenceIndex = 0;
Use these variables to track the longest sequence count, longest sequence value, and the starting index for the longest sequence.
Write a loop to read the input and update these variables. You don't need to store integers into an array or array list for this program.
Chapter 23: Programming Project 1
You may click Exercise23_11 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Use the code template from the project description to complete the exercise.
Chapter 24: Programming Project 1
You may click Exercise24_01 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Use the code template from the project description to complete the exercise.
The difference between Object[] toArray() and T[] toArray(T[] array)
is that you need to cast the element type to T. Here is the hing for implementing T[] toArray(T[] array):
@Override
public default <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
// Left as an exercise
for (int i = 0; i < size(); i++) {
a[i] = (T)[Write your code here]; // Assign each element in this MyList to a[i]
}
return a;
}
Chapter 24: Programming Project 2
You may click Exercise24_03 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Use the code template from the project description to complete the exercise.
Chapter 25: Programming Project 1
You may click Exercise25_01 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
For the definition of the height of a binary tree, see Section 25.2. Use recursion. If the tree is empty (i.e., root is null), return -1, else return 1 + the max of the height of the left and right subtrees.
Use the code template from the project description to complete the exercise.
Chapter 25: Programming Project 2
You may click Exercise25_03 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Copy the height() method from the preceding project. You can compare the tree size with 2^(height+1) - 1 to determine if the tree is perfect.
Chapter 25: Programming Project 3
You may click Exercise25_07 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Use recursion. If the tree is empty (i.e., root is null), return 0, else return 1 + the number of the non-leaf nodes in the left subtree + the number of the non-leaf nodes in the right subtree.
Chapter 25: Programming Project 4
You may click Exercise25_05Extra to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Use the code template from the project description to complete the exercise.
Chapter 26: Programming Project 1
You may click Exercise26_07 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Note the height() method is already given. Use recursion. If the tree is empty (i.e., root is null), return true, else do the following:
1. Get the height of the left subtree in height1.
2. Get the height of the right subtree in height2.
3. Return isAVLTree(root.left) && isAVLTree(root.right) && Math.abs(height1 - height2) <= 1.
Chapter 27: Programming Project 1
You may click Exercise27_01 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Please follow the template to complete the project.
Chapter 27: Programming Project 2
You may click Exercise27_11 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Use the code template from the project description to complete the exercise.
Chapter 28: Programming Project 1
You may click Exercise28_20Extra to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Use the code template from the project description to complete the exercise.
Chapter 28: Programming Project 2
You may click Exercise28_05 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Use the code template from the project description to complete the exercise.
Chapter 29: Programming Project 1
You may click Exercise29_04Extra to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Use the code template from the project description to complete the exercise.
Chapter 29: Programming Project 2
You may click Exercise29_05Extra to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Hint:
Use the code template from the project description to complete the exercise.
Chapter 30: Programming Project 1
You may click Exercise30_01 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Chapter 30: Programming Project 2
You may click Exercise30_07 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Chapter 30: Programming Project 3
You may click Exercise30_03 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Chapter 30: Programming Project 4
You may click Exercise30_13 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
Chapter 30: Programming Project 5
You may click Exercise30_11 to use the CheckExerciseTool to check and debug your code in addition to getting feedback from Revel. Please note that you need to change the class name to Exercise when submitting to Revel.
 If you use the AP version of the book, click
here.
If you use the AP version of the book, click
here.

 If you use the AP version of the book, click
here.
If you use the AP version of the book, click
here.

